√70以上 greenhouse gas emissions 236823-Greenhouse gas emissions definition
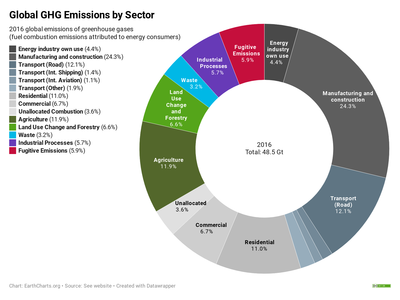
Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRL According to the 19 AGGI report, the combined heating influence of the longlived, humanproduced greenhouse gases is 314 Watts for every square meter of Earth's surface Just over 80 percent of that is due to carbon dioxide (66%) and methane (16%)Main Greenhouse Gases Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs lived Globally, the primary sources of greenhouse gas emissions are electricity and heat (31%), agriculture (11%), transportation (15%), forestry (6%) and manufacturing (12%) Energy production of all types accounts for 72 percent of all emissions

Saudi Arabia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Have Increased By 225 Since 1990 Climate Scorecard
Greenhouse gas emissions definition
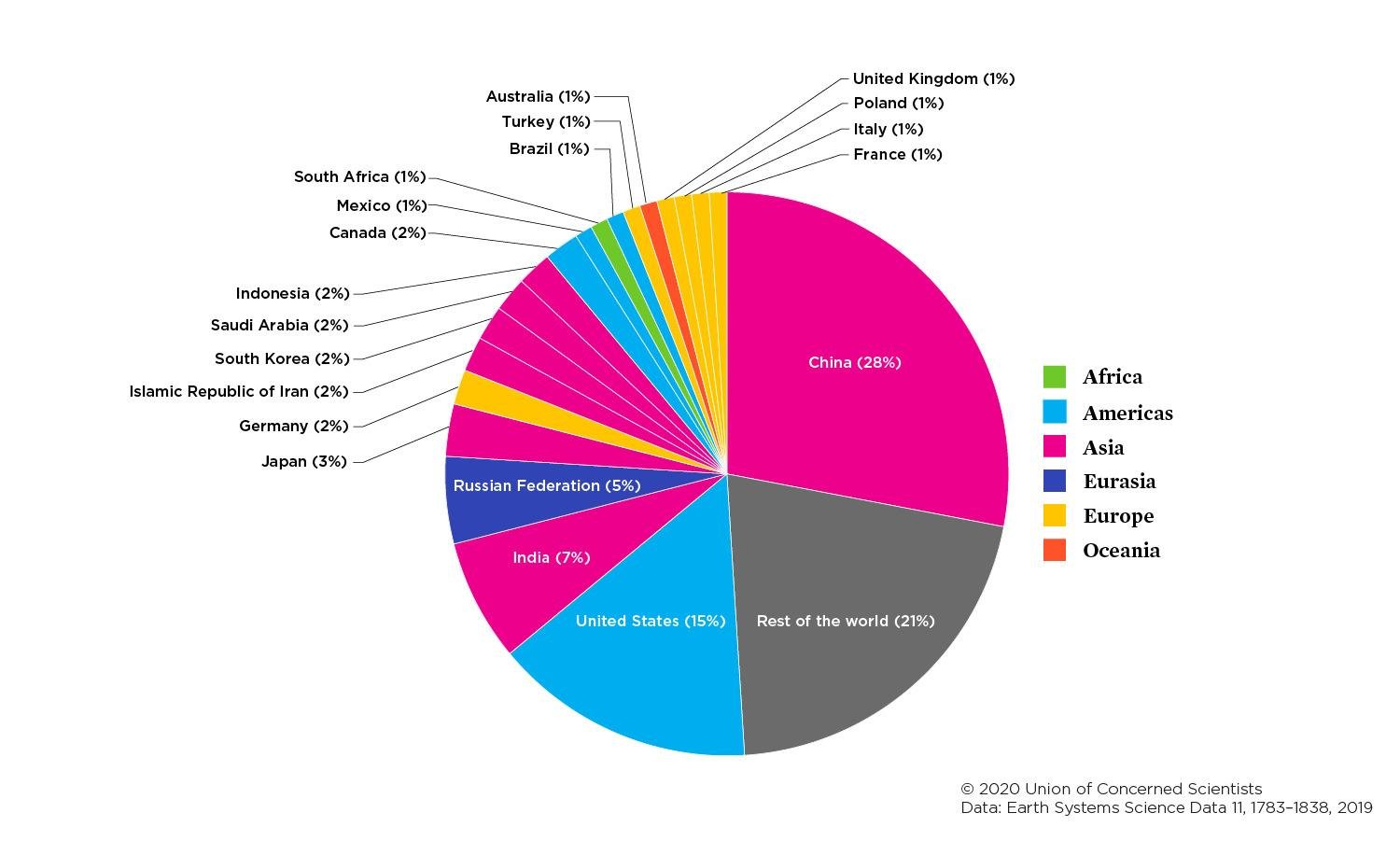
Greenhouse gas emissions definition- Global CO 2 emissions from coal use declined by almost 0 million tonnes (Mt), or 13%, from 18 levels, offsetting increases in emissions from oil and natural gas Advanced economies saw their emissions decline by over 370 Mt (or 32%), with the power sector responsible for 85% of the drop Milder weather in many large economies compared with 18 CO 2 emissions (total) 1 China 1006GT 2 United States 541GT 3 India 265GT 4 Russian Federation 171GT 5 Japan 116GT 6 Germany 075GT 7 Islamic Republic of Iran 072GT 8 South Korea 065GT 9 Saudi Arabia 062GT 10 Indonesia 061GT 11 Canada 056GT 12 Mexico 047GT 13 South Africa 046GT 14 Brazil 045GT 15 Turkey 042GT



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Oehha
Carbon dioxide (CO2) Carbon dioxide is the primary greenhouse gas, responsible for about threequarters of emissions It can linger in the The most significant greenhouse gases, according to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), are water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxideDeforestation and intensive agriculture also contribute greenhouse gas emissions, but not nearly as much as fossil fuel production, which accounts for 75 per cent of greenhouse gas emissions in North America As a result, the climate is changing worldwide That change has increased the severity and frequency of storms, heat waves, wildfires and
Policy Brief #52, by Jeffrey A Frankel (June 1999) Growth targets for emissions of greenhouse gases (GHG) by developing countries should be What are greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions? Food systems account for over onethird of global greenhouse gas emissions 9 March 21 Climate and Environment More than onethird of global greenhouse gas emissions caused by human activity can be attributed to the way we produce, process and package food, a UNbacked study published on Tuesday has revealed /Johannes Plenio
Emissions of several important greenhouse gases that result from human activity have increased substantially since largescale industrialization began in the mid1800s Most of these humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gas emissions were carbon dioxide (CO2) from burning fossil fuelsAs we confront climate change, focusing on a single metric, like greenhouse gas emissions, could leave other harmful practices unaddressed By Marty Mulvihill, Gretta Goldenman and Arlene BlumFalling by 438 per cent between 1990 and 18 and



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia



Rggi
The impact of food on greenhousegas (GHG) emissions can slip under the radarIn a survey in Britain last year, the share of respondents saying that 19 UK greenhouse gas emissions final figures xlsx and ods data tables updated New annex added final emissions by end user and fuel type 2 February 21 Territorial emissions of greenhouse gases by sector (million tonnes carbon dioxide equivalent) Data collection and calculation All emission estimates include the basket of 7 Kyoto greenhouse gases in kilotonnes of CO2 equivalent Data in this cube currently excludes emissions from international aviation and shipping



Each Country S Share Of Co2 Emissions Union Of Concerned Scientists




How Trump Is Ensuring That Greenhouse Gas Emissions Will Rise The New York Times
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 14, CO 2 accounted for about 809% of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and animals)Australian Greenhouse Emissions Information System The AGEIS is an online database that provides detailed greenhouse gas emissions data from the National Greenhouse Accounts—with the exception of Quarterly updates Data can be queried through a dynamic interface and search function View the Australian Greenhouse Emissions Information System (AGEIS)Between 08 and 19 the level of greenhouse gas emissions from the supply of electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning fell by 381 million tonnes of CO 2 equivalents, a fall of 31 % in relative terms Both in absolute and relative terms, this was the largest decrease recorded among the activity groupings studied




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Decreased In Germany By 42 Compared To 1990 Levels Climate Scorecard




Greenhouse Gas Emissions To Set New Record This Year But Rate Of Growth Shrinks Science as
In 18, gross greenhouse gas emissions were 7 million tonnes of CO₂e, 240 percent higher than 1990 and 10 percent lower than 17There are two types of emissions that impact on the environment Greenhouse gas emissions, such as carbon dioxide (CO 2), which can trap additional heat from the sun in the earth's atmosphere, causing the 'greenhouse effect' and climate changeCO 2 is the main greenhouse gas produced by motor vehicles In 17, the average combined CO 2 emissions for a new light Almost none of these emissions are included in the UK's national greenhouse gas inventory;




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Santa Fe City Of Santa Fe New Mexico
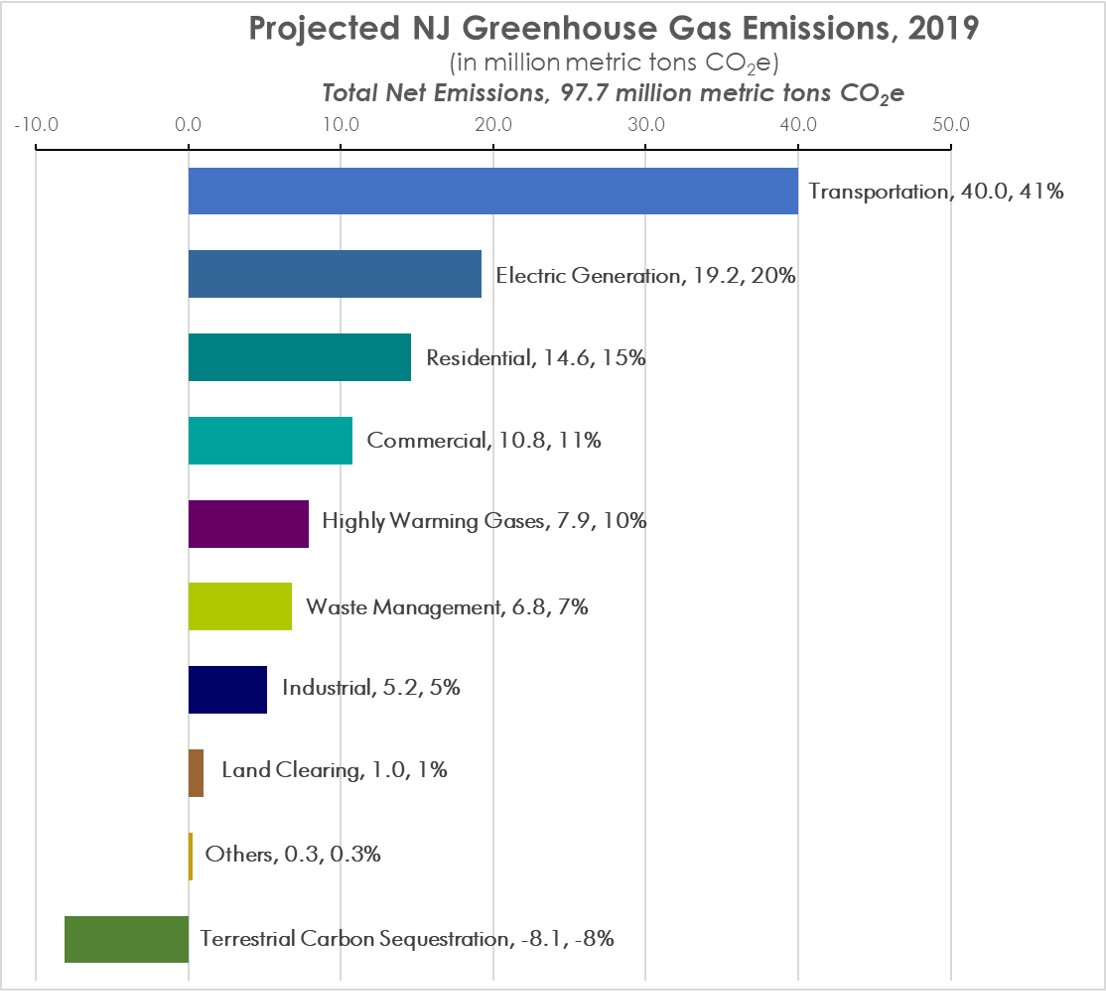



Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability
The UK produces an annual greenhouse gas inventory, a consistent time series of UK greenhouse gas emissions from 1990 onwards Official statistics on UK greenhouse gas emissions are also producedGreenhouse gases refer to the sum of seven gases that have direct effects on climate change carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3) The data are expressed in CO 2 equivalents and refer to gross direct emissionsAs we discussed in the previous sections, total greenhouse gas emissions are the sum of emissions of various gases carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and smaller trace gases such as hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) and sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) How much does each gas contribute to global greenhouse gas emissions?
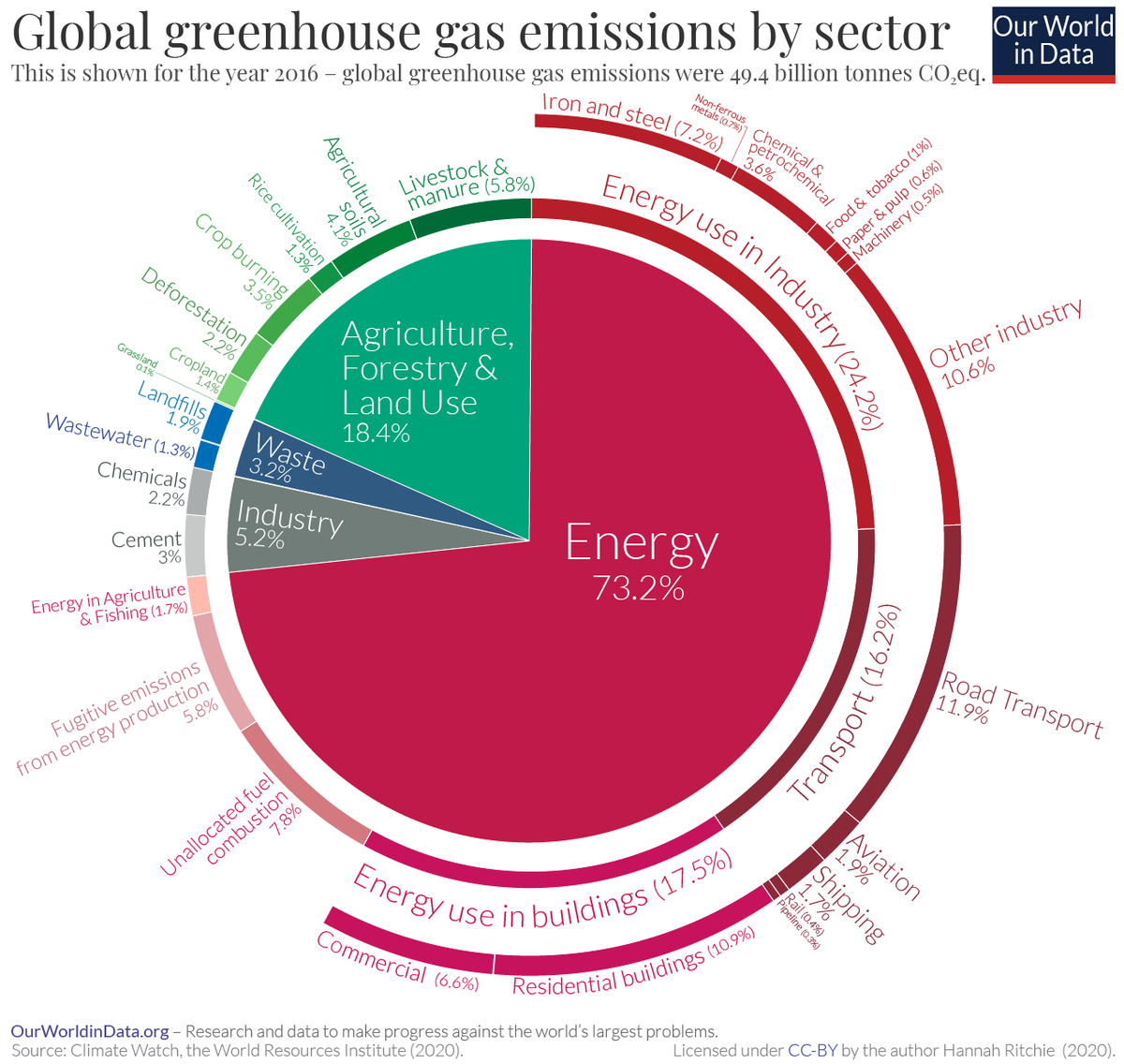



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector
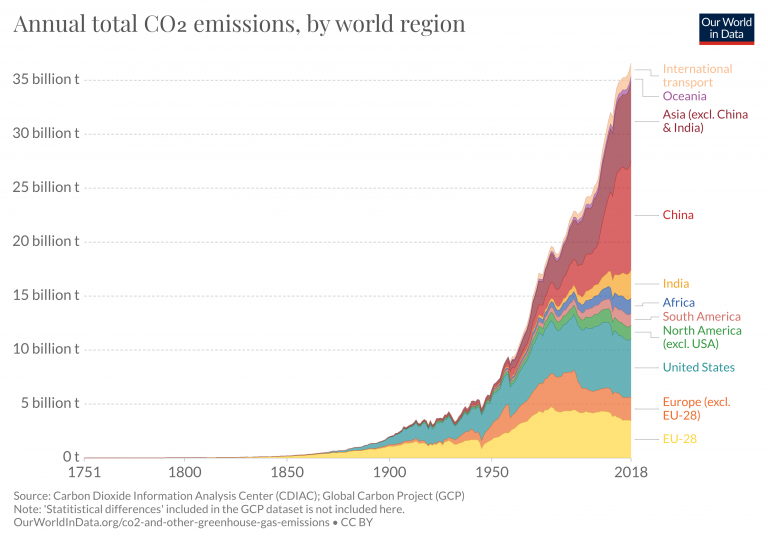



Co2 Emissions Our World In Data
Greenhouse gas emissions definition the emission into the earth's atmosphere of any of various gases , esp carbon dioxide , Meaning, pronunciation, translations and examplesContinued emission of greenhouse gases will cause further warming and longlasting changes in all components of the climate system, increasing the likelihood of severe, pervasive and irreversible impacts for people and ecosystems Limiting climate change would require substantial and sustained reductions in greenhouse gas emissions whichMeasuring greenhouse gas emissions using nuclear techniques To reduce the emission of nitrous oxide, a greenhouse gas with a global warming potential 300 times larger than that of carbon dioxide, chemical fertilizers, pesticides and manure must be used conscientiously




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Oehha




Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
15 hours ago An extra £350m is promised to help the automotive supply chain move to electric The new plan set out by the government is supposed to dramatically reduce greenhouse gas emissions to reach aHuman emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases – are a primary driver of climate change – and present one of the world's most pressing challenges 1 This link between global temperatures and greenhouse gas concentrations – especially CO 2 – has been true throughout Earth's history 2Greenhouse gas emissions from the oil and gas sector Key results In 19, the oil and gas sector was the largest source of GHG emissions, accounting for 26% of total
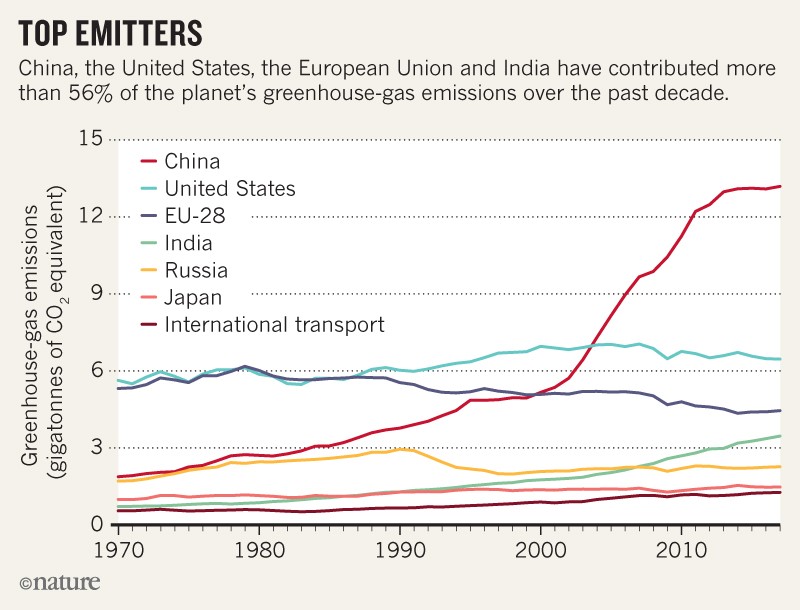



Nations Must Triple Efforts To Curb Greenhouse Gas Emissions



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
Greenhouse gas emissions decreased by 9 per cent According to Statistics Finlands instant preliminary data, the total emissions of greenhouse gases in corresponded with 4 million tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2 eq) Compared with the previous year, emissions decreased by nine per cent, so that total greenhouse gas emissions can be reported on a consistent basis The GWP for each gas is defined as its warming influence relation to that of carbon dioxide over a 100year period Greenhouse gas emissions are then presented in carbon dioxide equivalent units (CO 2 e)Greenhouse Gas Emissions A gas that absorbs heat within a planet's atmosphere, causing the greenhouse effect Greenhouse gases on earth include carbon dioxide, water vapour, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia
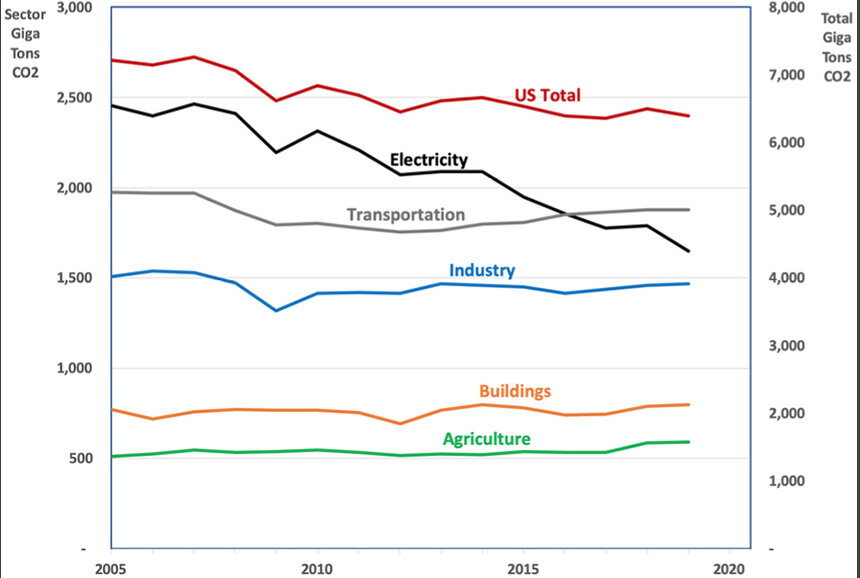



No Progress Made To Reduce U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ecori News
Greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are the gases that are released into the atmosphere as a result of certain activities GHGs are accumulating in the atmosphere like a blanket, trapping heat and raising global temperatures GHG emissions come from activities like driving, heating buildings, powering industry, farming and There are two measures of greenhouse gases presented in this release SOURCE EMISSIONS A measure of the actual emissions or removals of greenhouse gases in Scotland, including international aviation and shipping Source emissions were 478 million tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent in 19;Emissions Driven by higher energy demand in 18, global energyrelated CO2 emissions rose 17% to a historic high of 331 Gt CO2 While emissions from all fossil fuels increased, the power sector accounted for nearly twothirds of emissions growth Coal use in power alone surpassed 10 Gt CO2, mostly in Asia
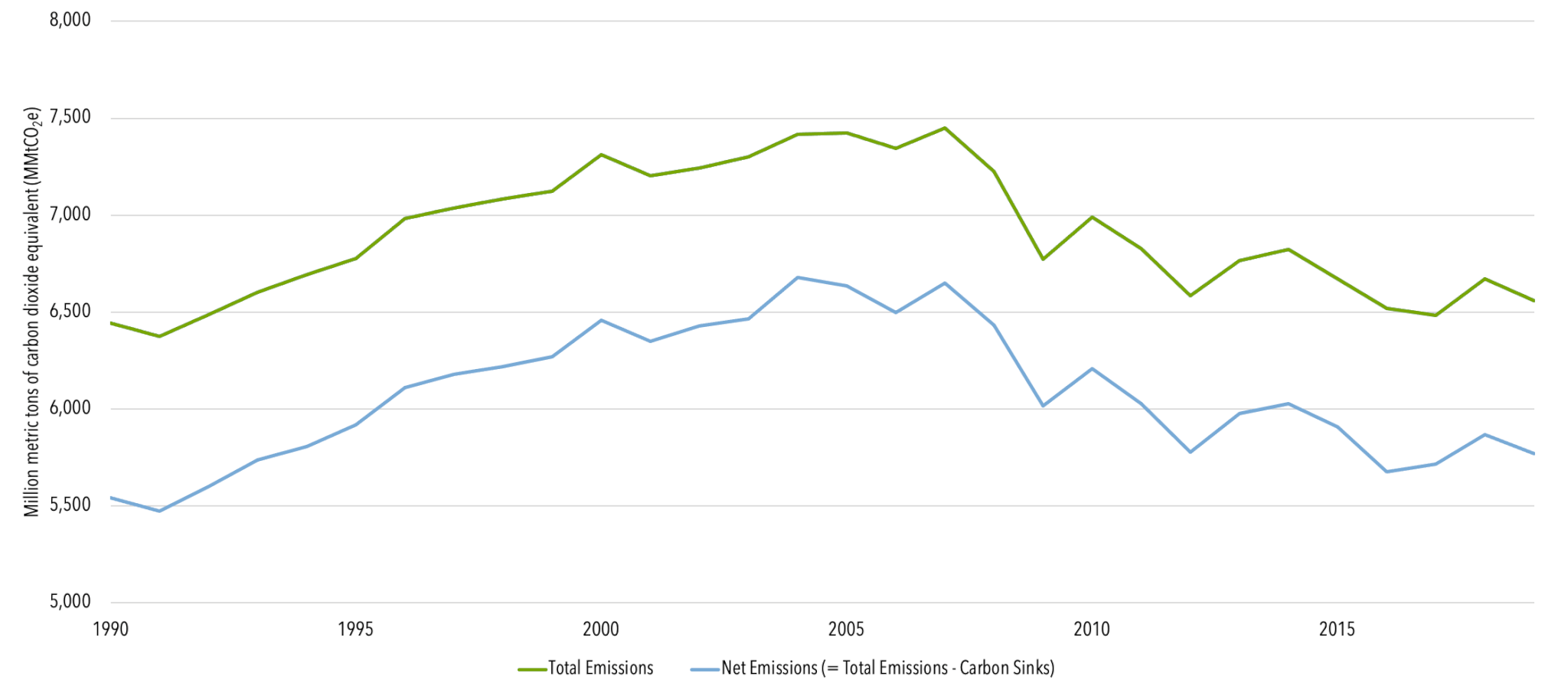



U S Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions



Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends European Environment Agency
Electricity Sector Emissions Total Emissions in 14 = 6,870 Million Metric Tons of CO 2 equivalent * Land Use, LandUse Change, and Forestry in the United States is a net sink and offsets approximately 11 percent of these greenhouse gas emissions All emission estimates from the Inventory of US Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks 1990–14 Larger image to save orIf they were, this would have added between 22 and 27 per cent to the emissions from total UK electricity generation, or 28–36 per cent of total UK greenhouse gas emissions in 19Greenhouse gas, any gas capable of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the phenomenon known as the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor are the most important greenhouse gases



Co And Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data
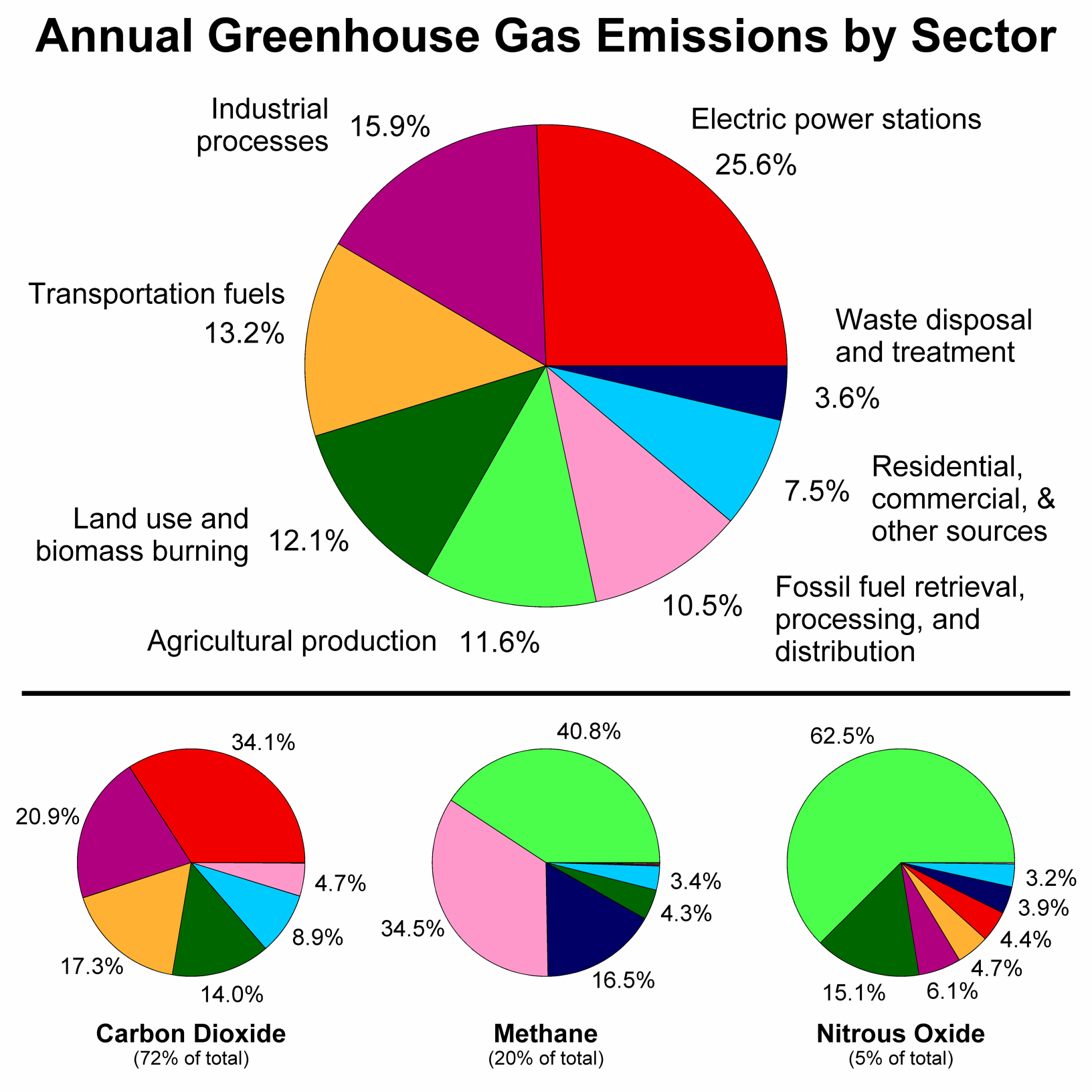



File Greenhouse Gas By Sector Png Wikimedia Commons




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Shipping Shell Global




Australia Yearly Greenhouse Gas Emissions Statista




Saudi Arabia Greenhouse Gas Emissions Have Increased By 225 Since 1990 Climate Scorecard
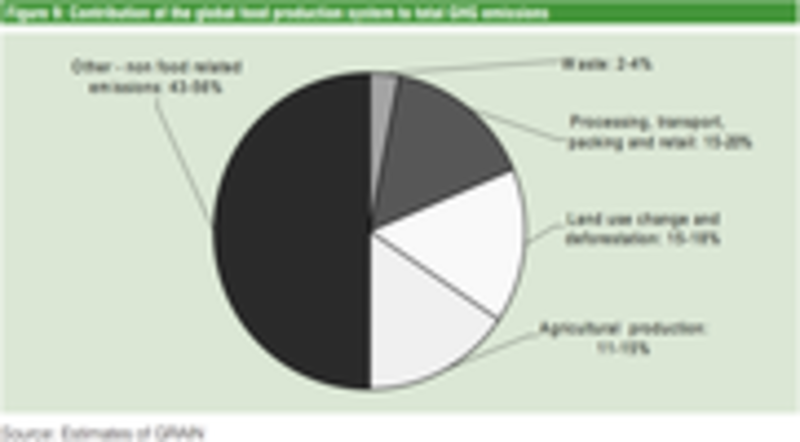



Grain How Much Of World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Agriculture




Why Are Ontario S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Going Up Instead Of Down Environmental Defence



Fossil Fuels
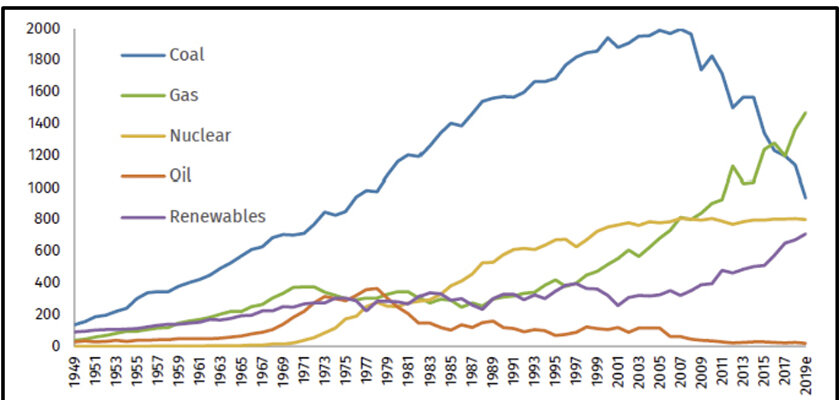



No Progress Made To Reduce U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Ecori News




Forecast U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions To Fall 7 5 Percent In Mpr News
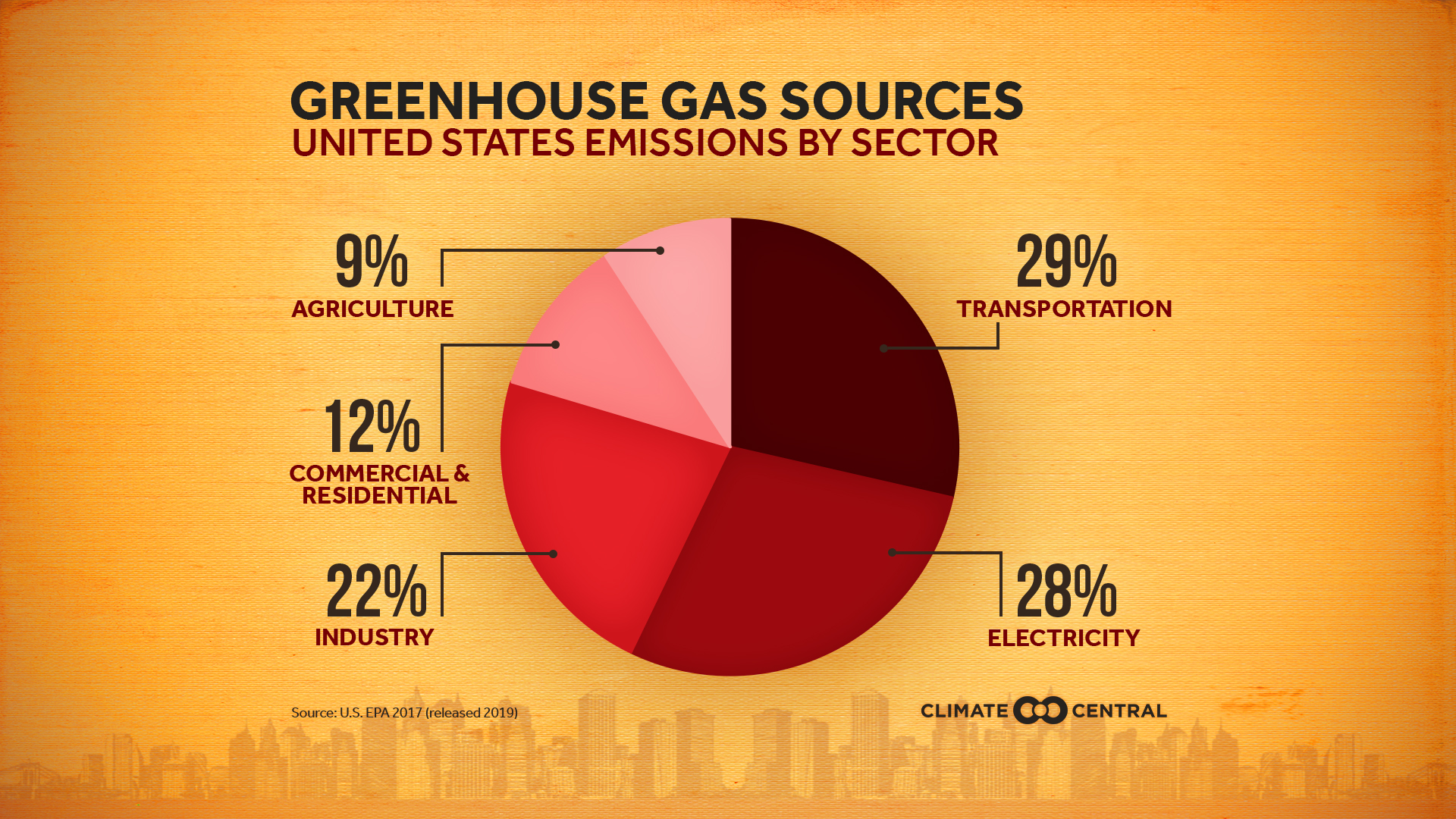



Emissions Sources Climate Central




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament




Ending Greenhouse Gas Emissions May Not Stop Global Warming Study
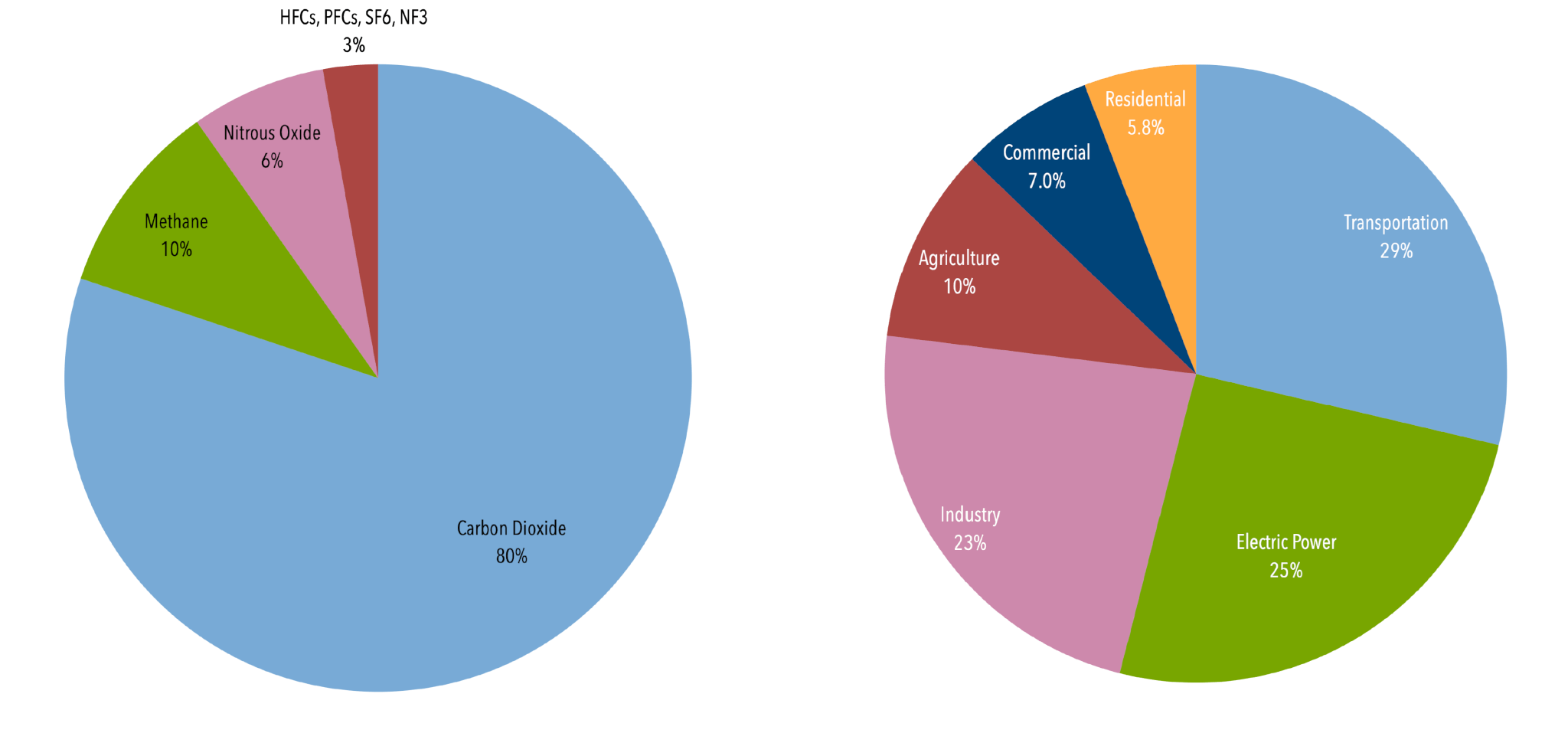



U S Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions
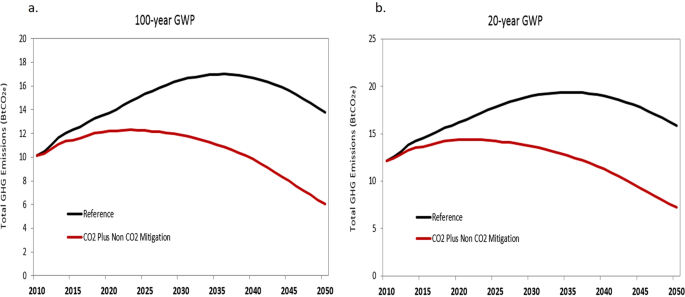



China S Non Co2 Greenhouse Gas Emissions Future Trajectories And Mitigation Options And Potential Scientific Reports
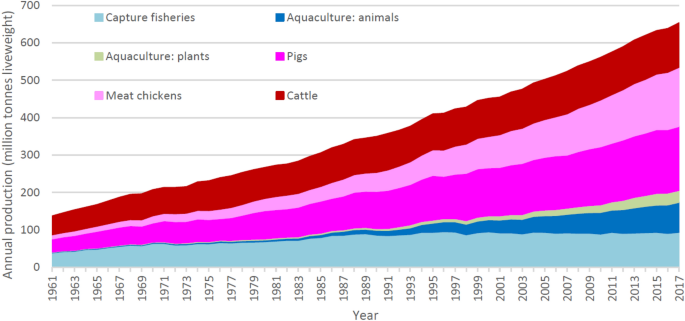



Quantifying Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Global Aquaculture Scientific Reports
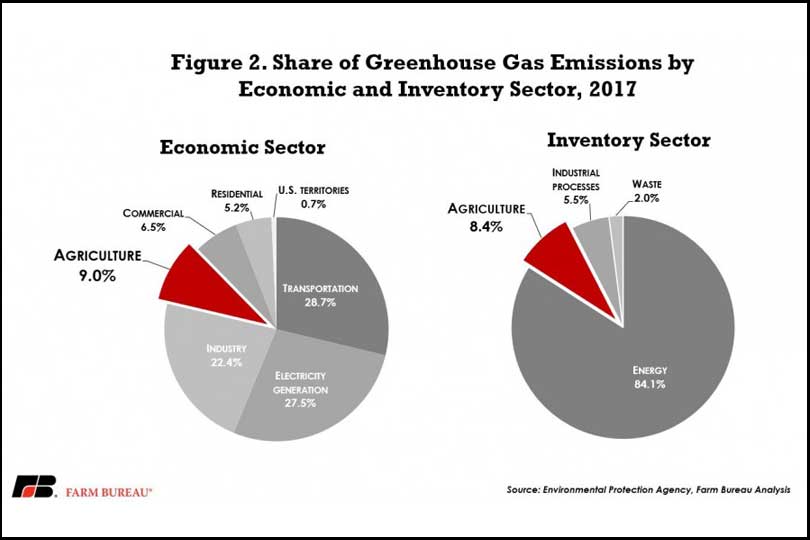



Report Clears Air On Greenhouse Gas Emissions For Cattle Texas Farm Bureau




France Greenhouse Gas Emissions Decreased By 16 9 From 1990 Levels Climate Scorecard
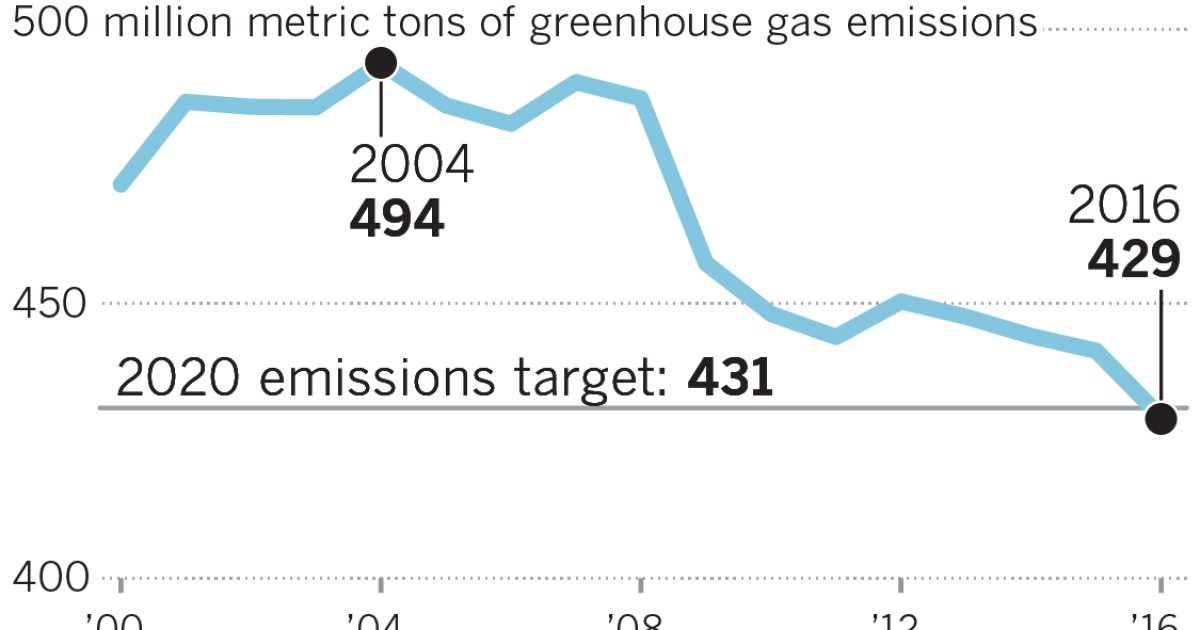



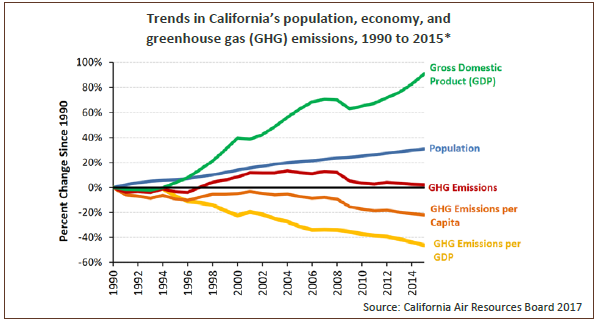
California Hit Its Climate Goal Early But Its Biggest Source Of Pollution Keeps Rising Los Angeles Times




Where Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From University Of California



Rudn University Ecologist Suggested A Way To Eurekalert




Where Do Canada S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From




U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions 1990 19 Statista



1
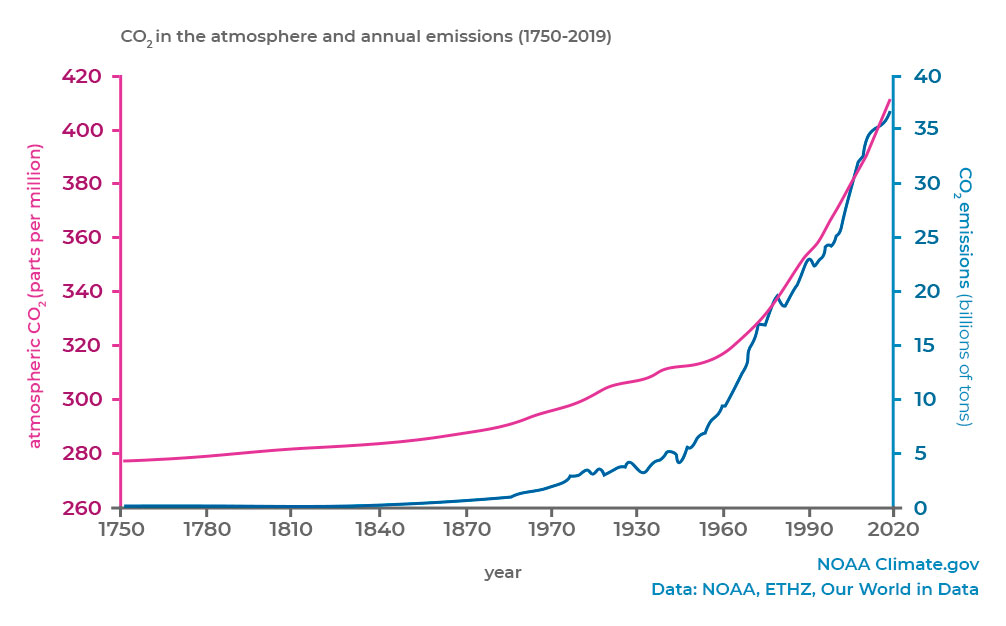



Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Proterra Foundation




Eu Greenhouse Gas Emissions 1990 18 Statista




Nigeria Has Experienced A 271 Increase In Greenhouse Gas Emissions Since 1990 Climate Scorecard




More Firms Pledge To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions Marketplace



Eco Economy Indicators Carbon Emissions Epi
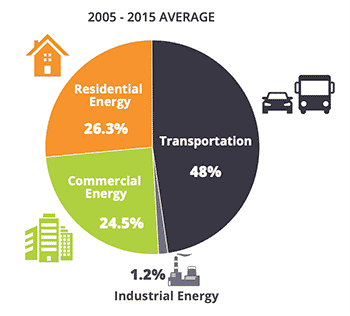



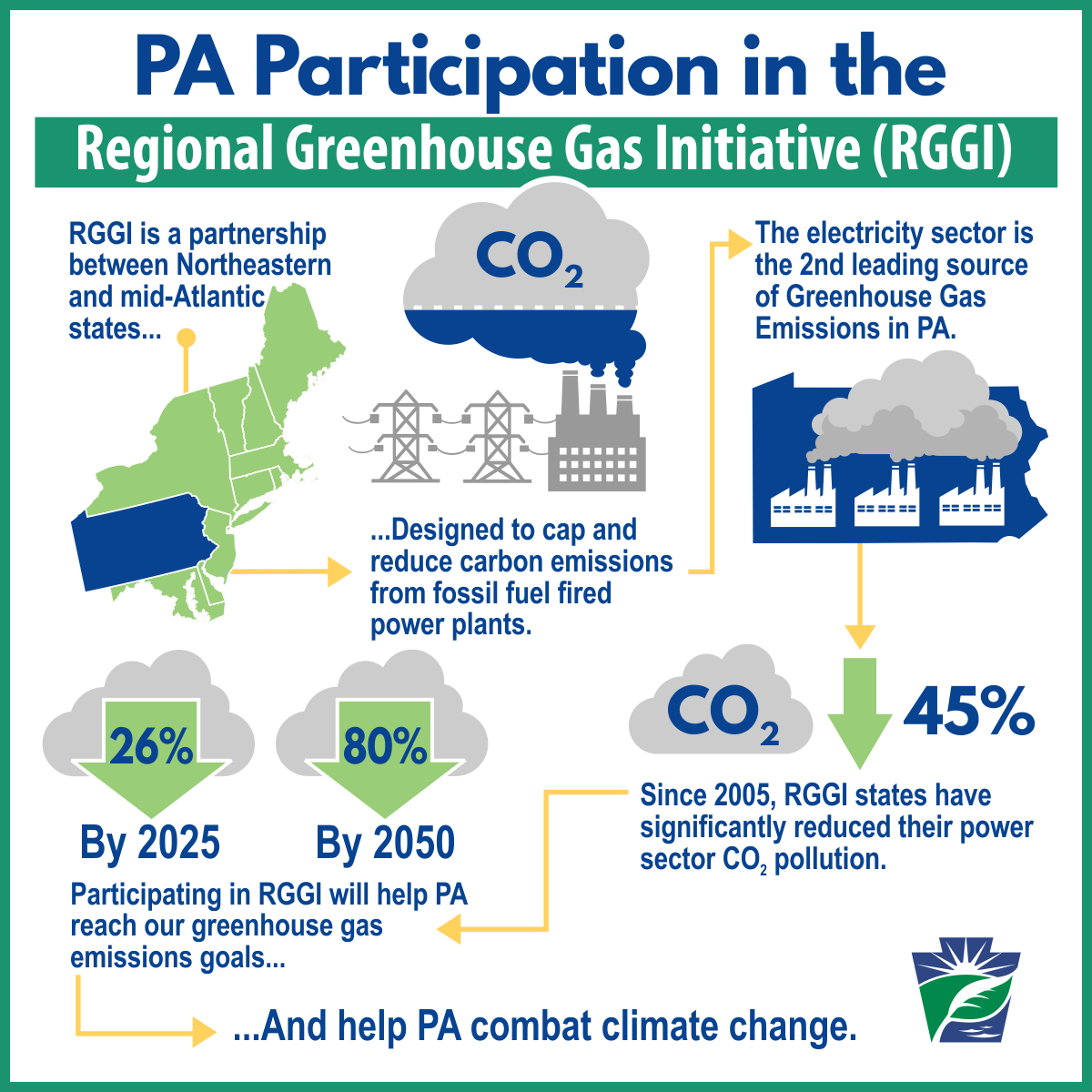
Regional Greenhouse Gas Inventory Transportation And Stationary Energy Southeast Florida Regional Climate Compact




Scottish Greenhouse Gas Emission Rates Halved Since 1990 c News




New Study Food Systems Responsible For 34 Of Human Caused Ghg Emissions Not 25 As Previously Thought
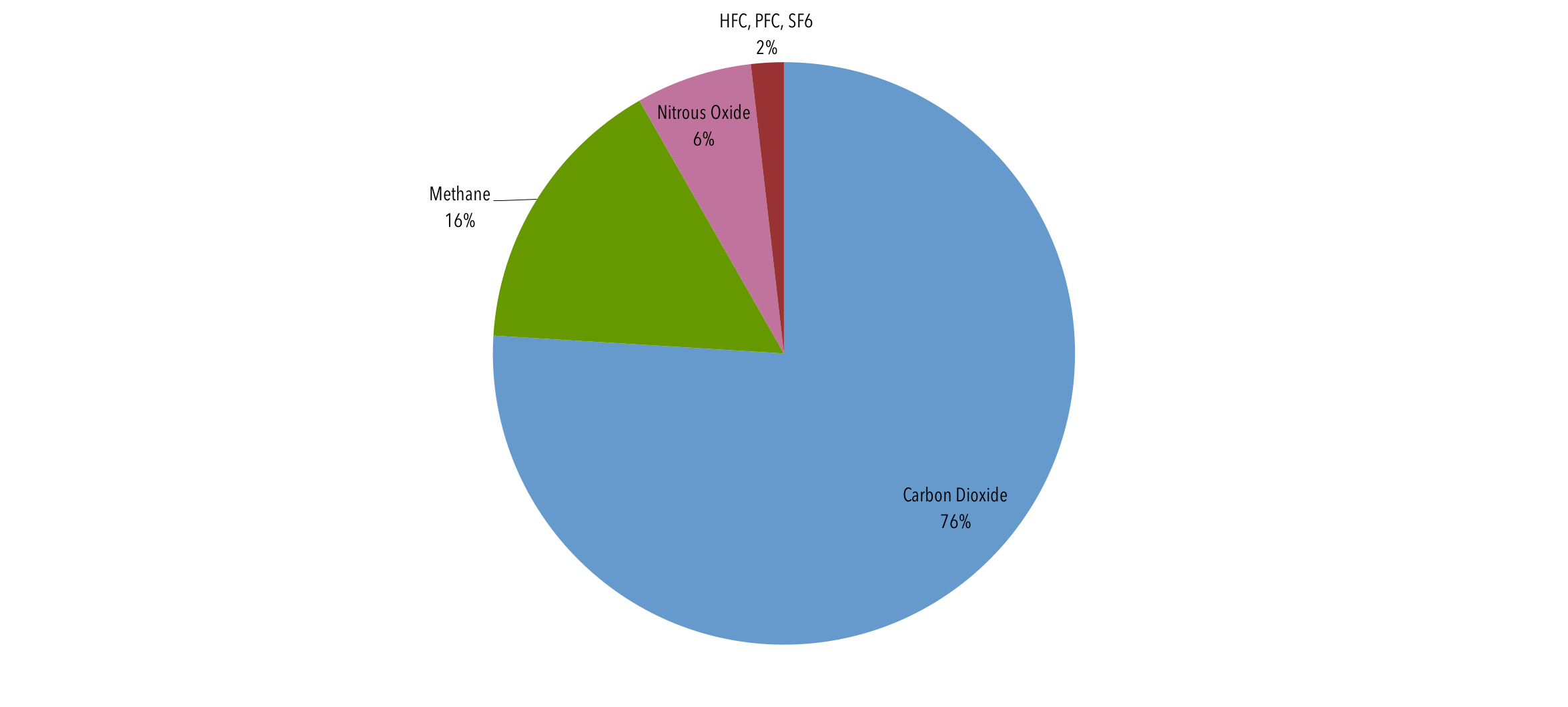



Global Emissions Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Uk Fell 3 In 18 Official Figures Show Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Guardian
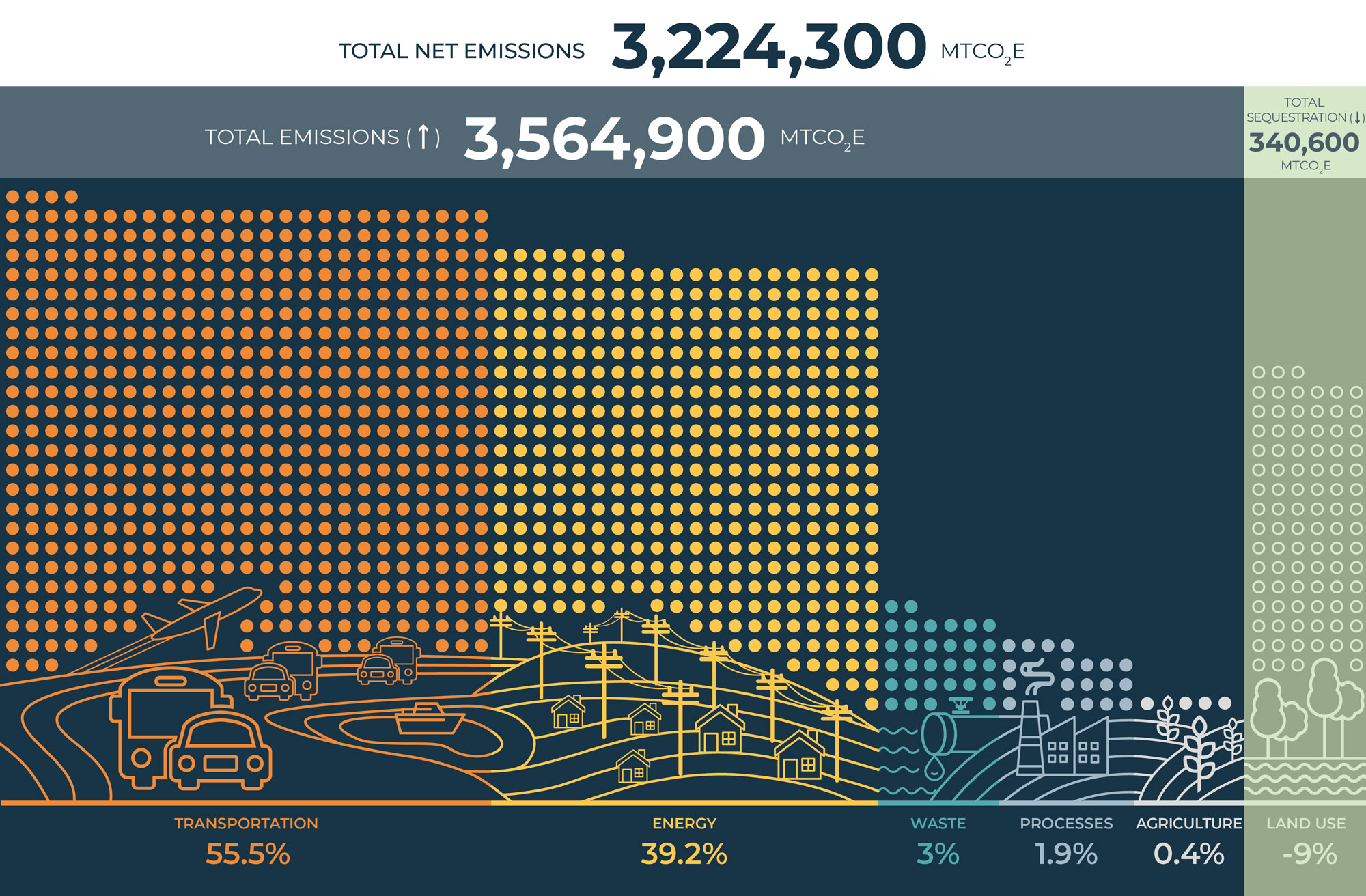



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Cape Cod Commission




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By The United States Wikipedia




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
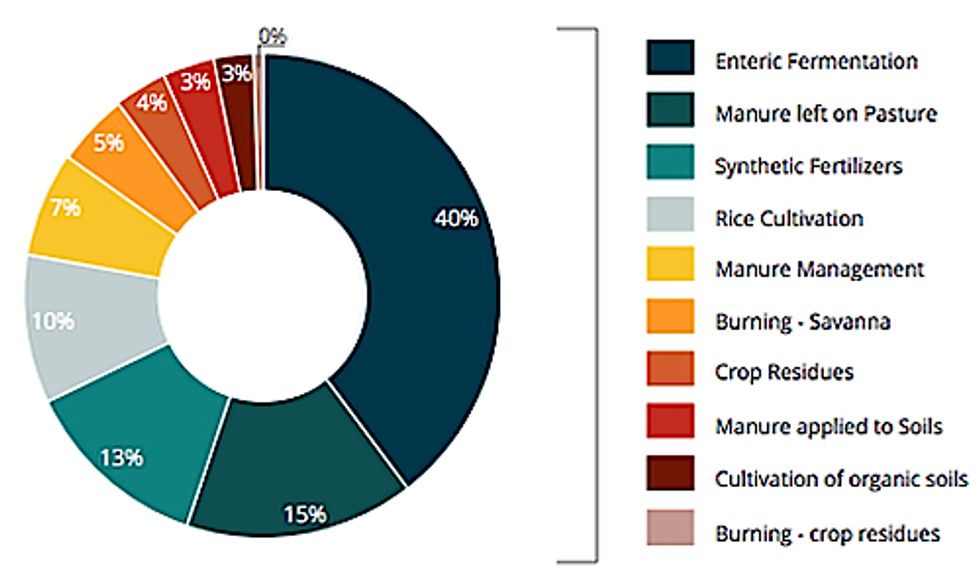



Un Predicts 30 Rise In Agriculture S Greenhouse Gas Emissions By 50 Ecowatch




Industry Contribution To Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Energy Innovation Policy And Technology



Total Greenhouse Gas Emission Trends And Projections In Europe European Environment Agency




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




Uzccvmewarjbxm




Germany S Greenhouse Gas Emissions And Energy Transition Targets Clean Energy Wire




Since 1990 Greenhouse Gas Emissions Have Increased By 2 7 In Japan Climate Scorecard




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament



1
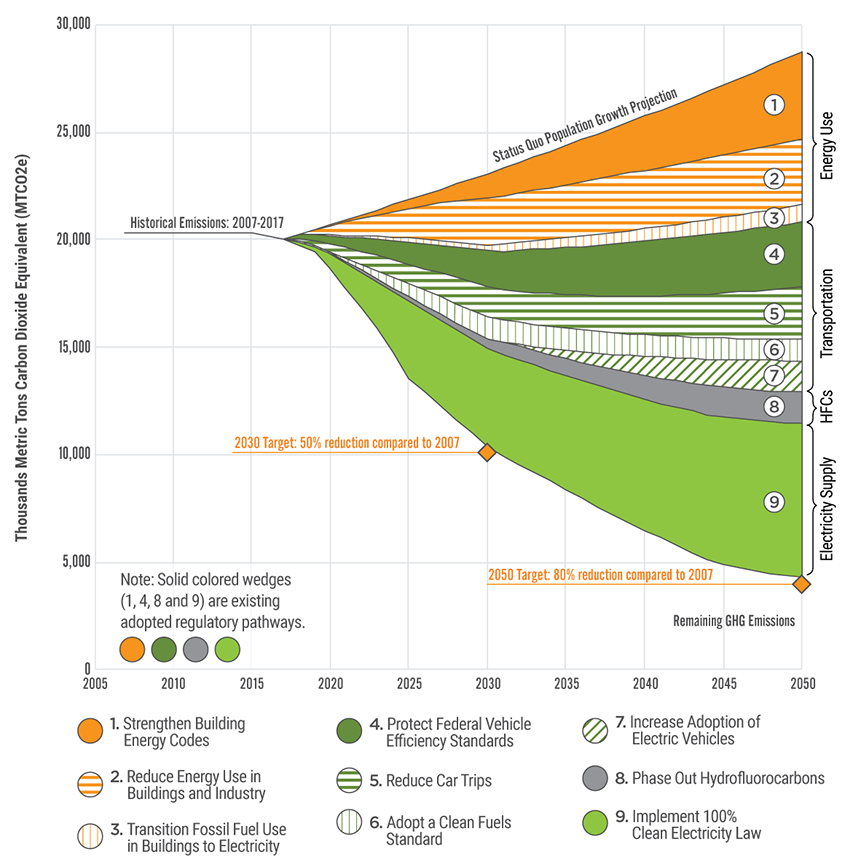



King County Greenhouse Gas Emissions King County




Scale Distribution And Variations Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Driven By U S Households Sciencedirect



1
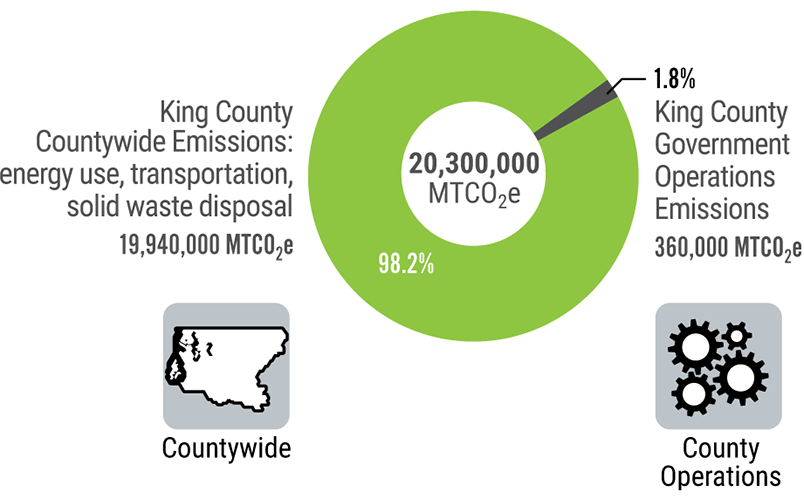



King County Greenhouse Gas Emissions King County
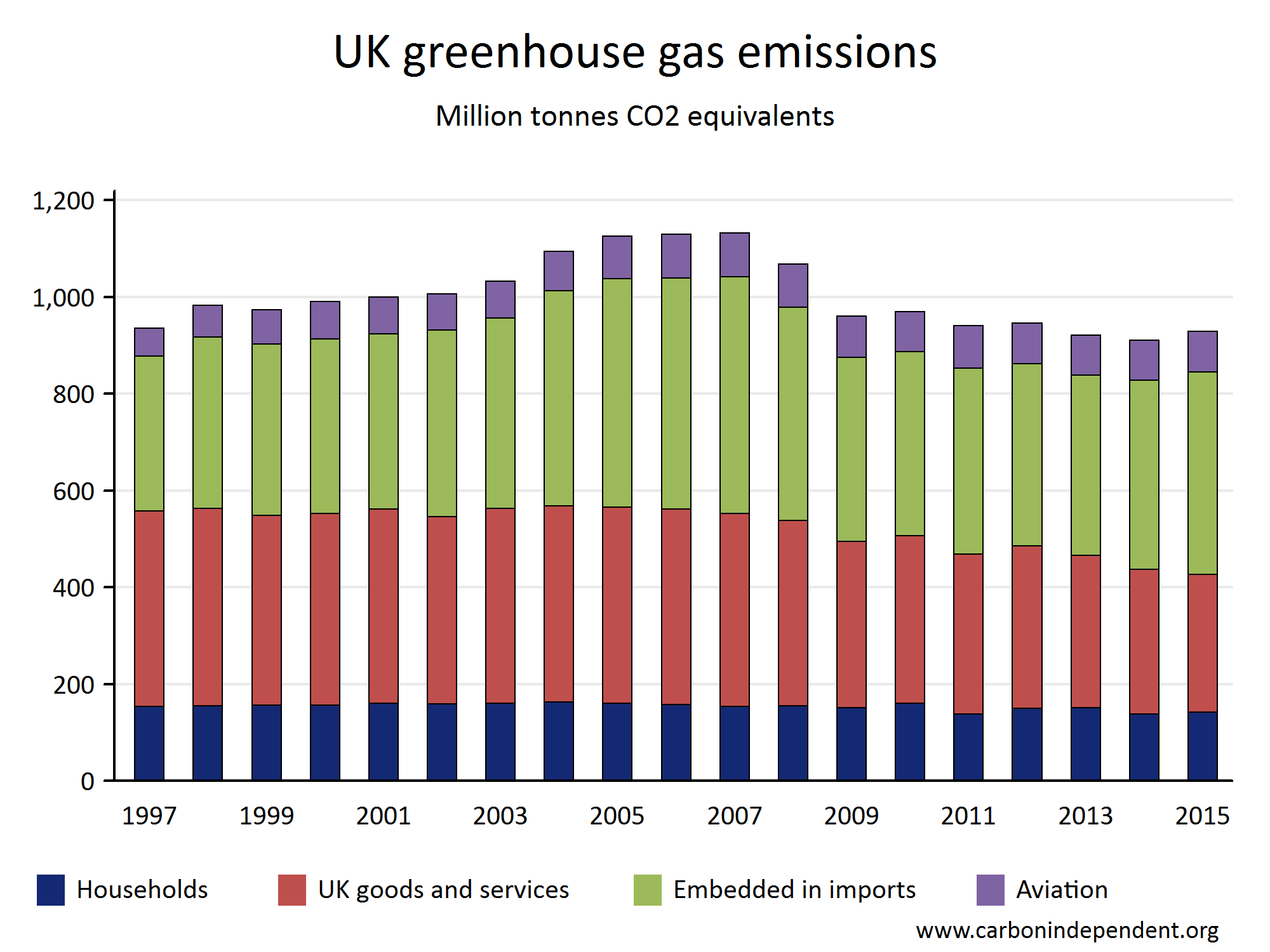



The Uk Has Not Cut Its Greenhouse Gas Emissions
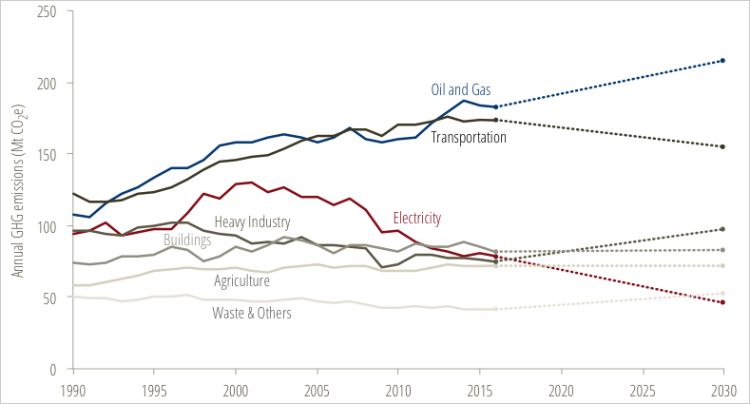



Three Takeaways From Canada S Latest Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Blog Posts Pembina Institute
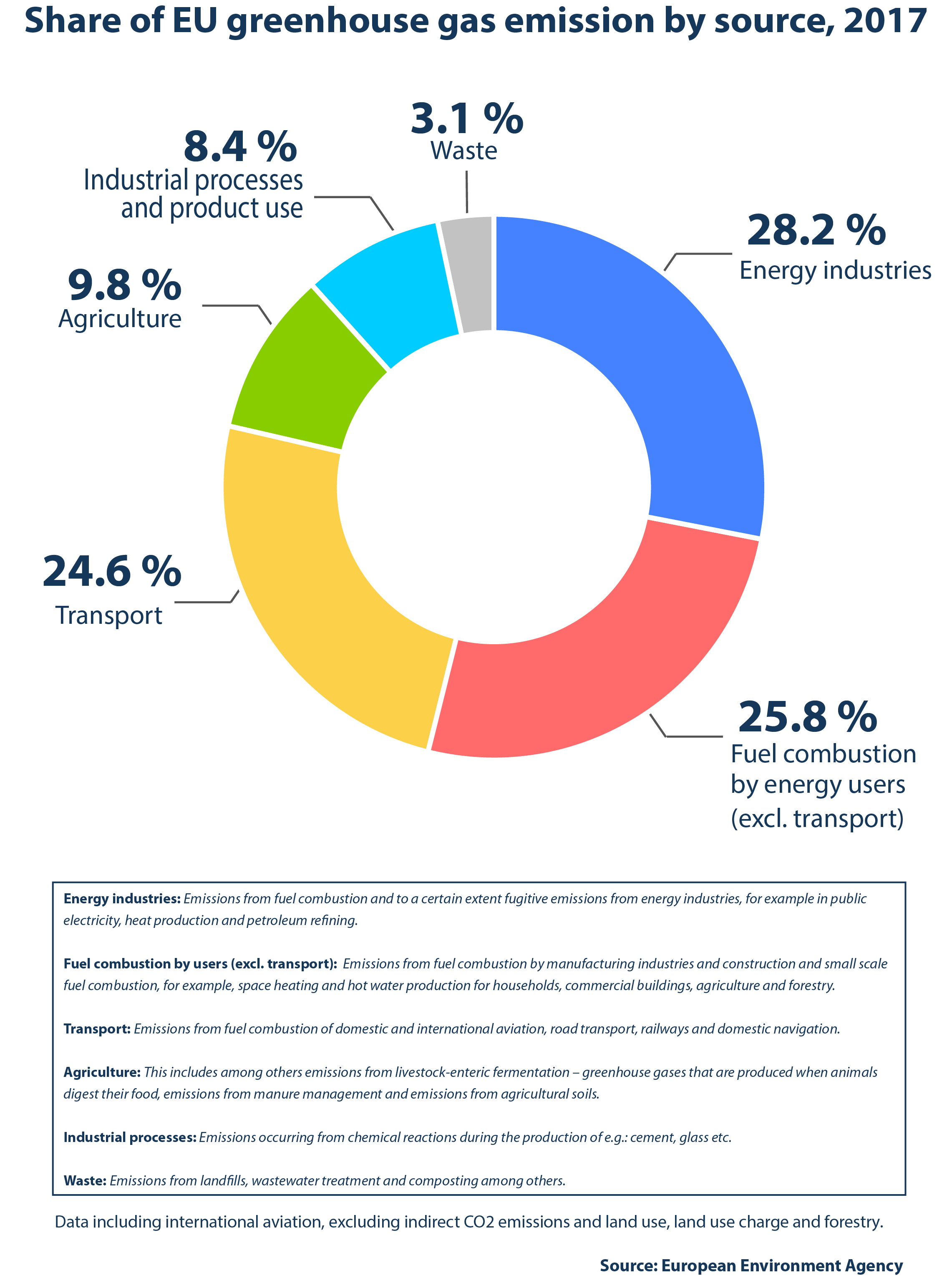



How Are Emissions Of Greenhouse Gases By The Eu Evolving




Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions Can Improve Air Quality And Save Lives




Transport Could Burn Up The Eu S Entire Carbon Budget International Council On Clean Transportation
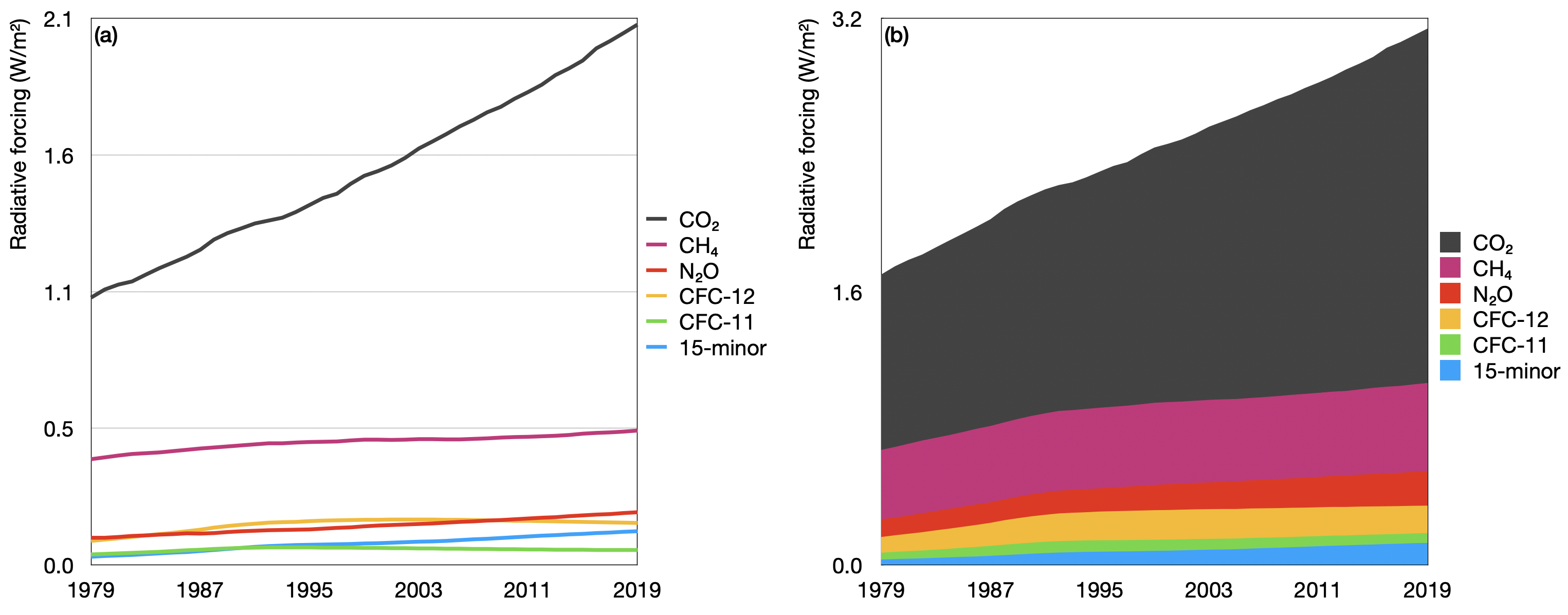



Greenhouse Gas Emissions World Energy Data




Just 100 Companies Responsible For 71 Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Report Says The Independent The Independent
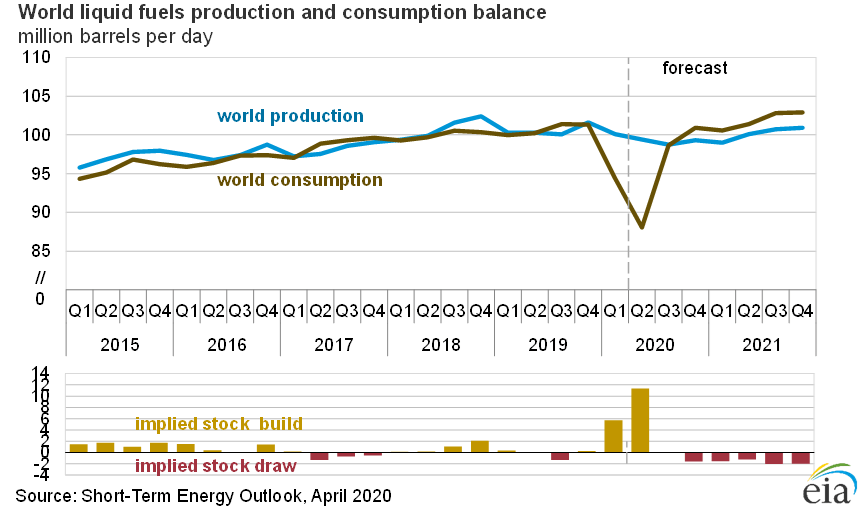



Forecast U S Greenhouse Gas Emissions To Fall 7 5 Percent In Mpr News




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Factsheet Brazil Global Climate Change




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Are Set To Rise Fast In 21 The Economist
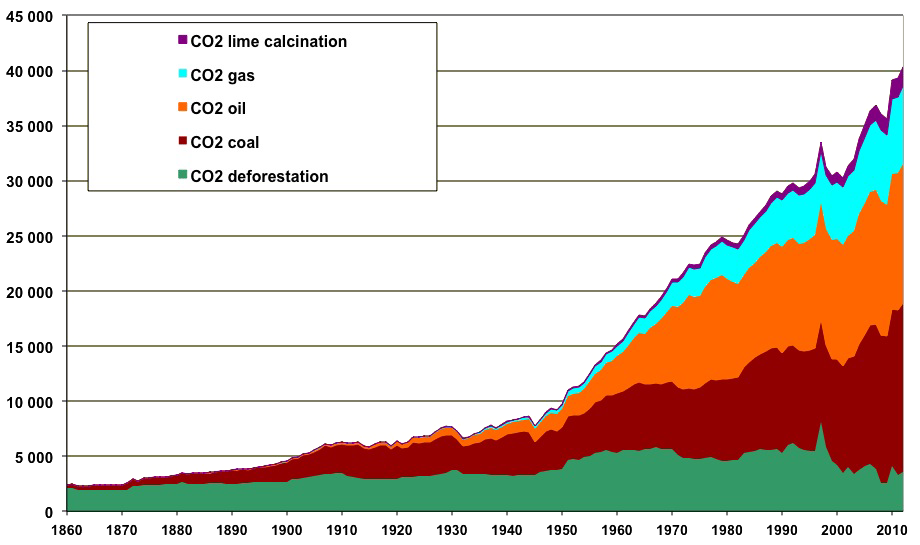



How Do Greenhouse Gas Emissions Presently Evolve Jean Marc Jancovici




What S The Deal With Greenhouse Gases Emissions And The Environment Futurelearn




Drivers Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Africa Focus On Agriculture Forestry And Other Land Use Our Africa Our Thoughts




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa




California Plans To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions 40 By 30 Today In Energy U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
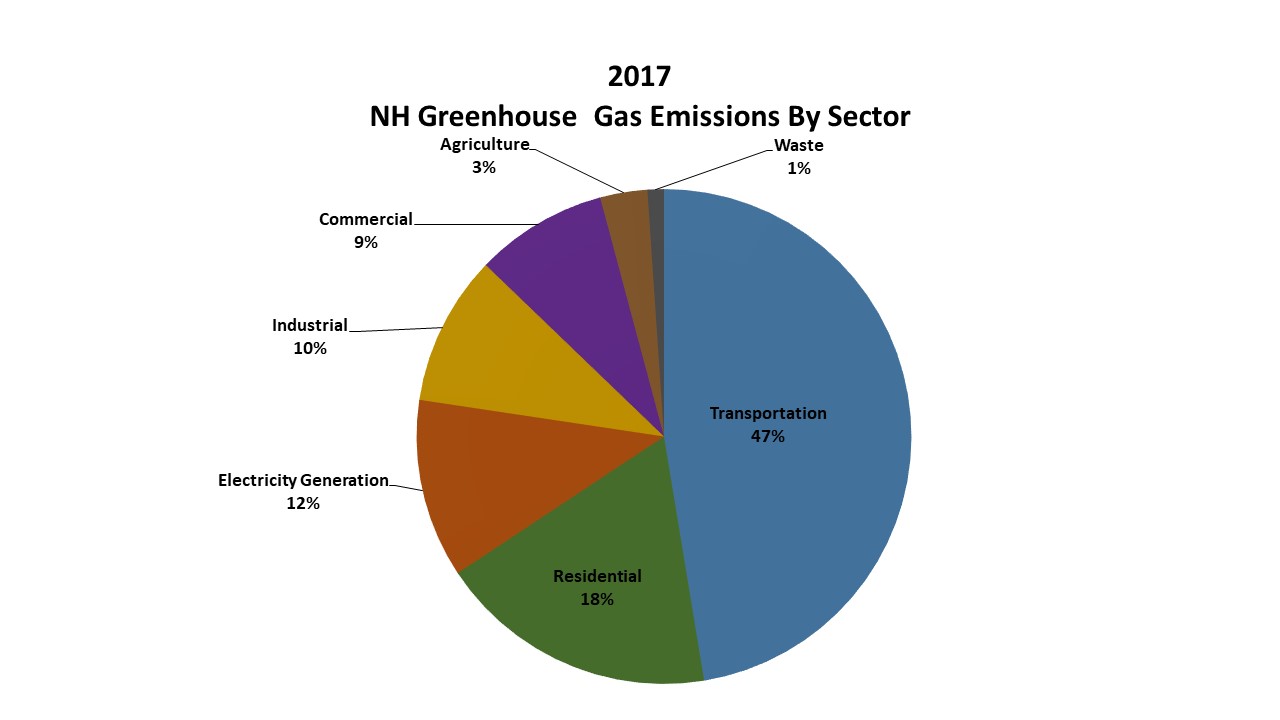



Greenhouse Gas Emissions Inventory Nh Department Of Environmental Services




Greenhouse Gas Emissions In Agriculture Proterra Foundation
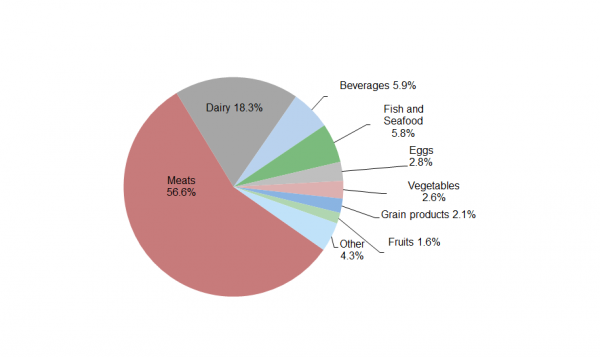



Carbon Footprint Factsheet Center For Sustainable Systems




Food Production Is Responsible For One Quarter Of The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Federal Climate Policy To Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions




Russia Passes First Law To Limit Greenhouse Gas Emissions The Moscow Times




4 Charts Explain Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Countries And Sectors Thecityfix




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gas Ghg Emissions Inventory Partner Energy



Ghg Reduction Sustainability And Public Health Mndot
.png)



Climate Change In Illinois Climate
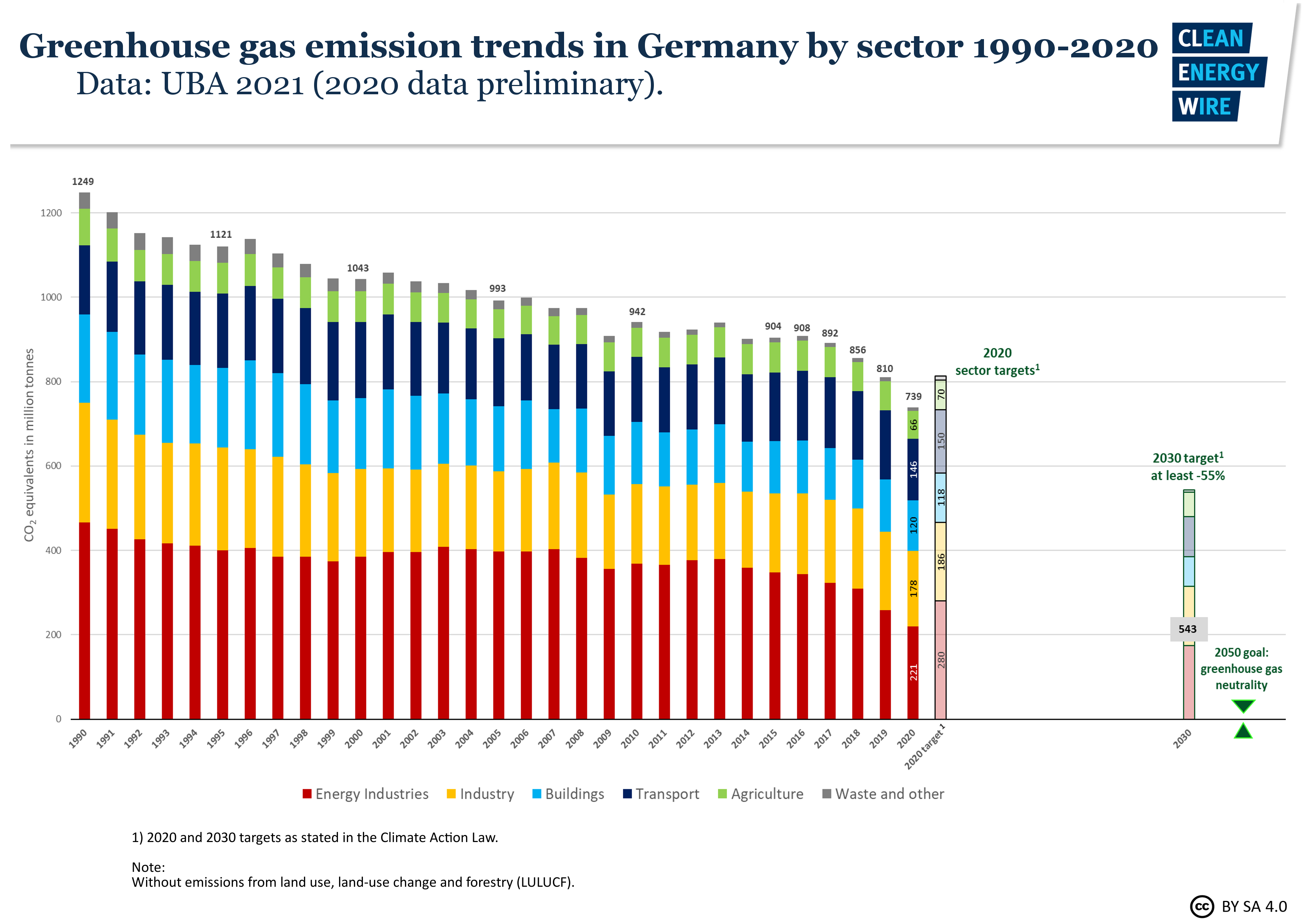



Germany Sees Record Greenhouse Gas Emission Fall Due To Pandemic Renewables Clean Energy Wire
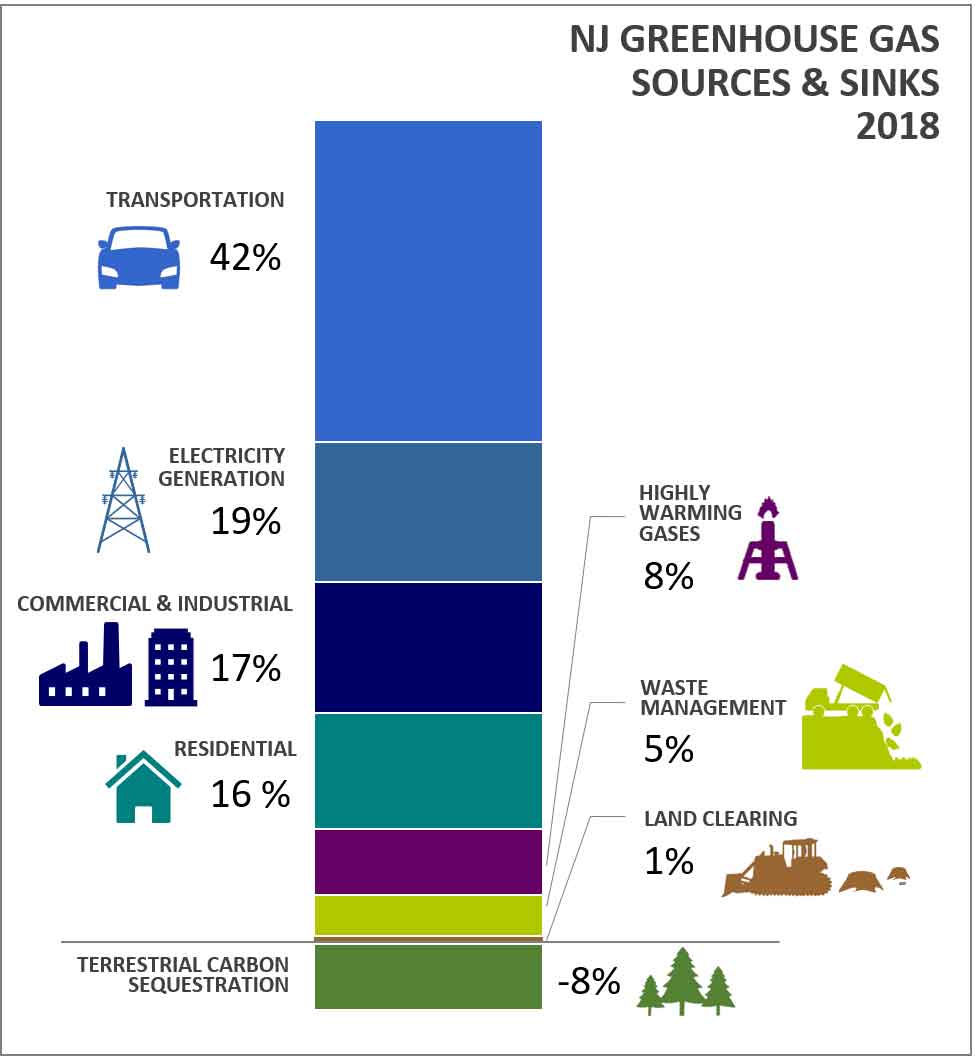



Njdep Air Quality Energy Sustainability
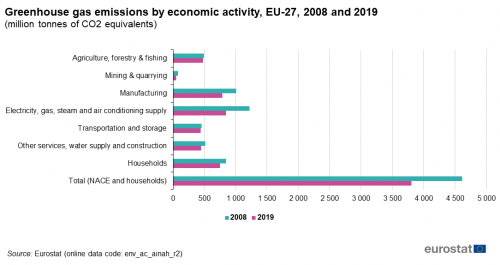



Greenhouse Gas Emission Statistics Air Emissions Accounts Statistics Explained
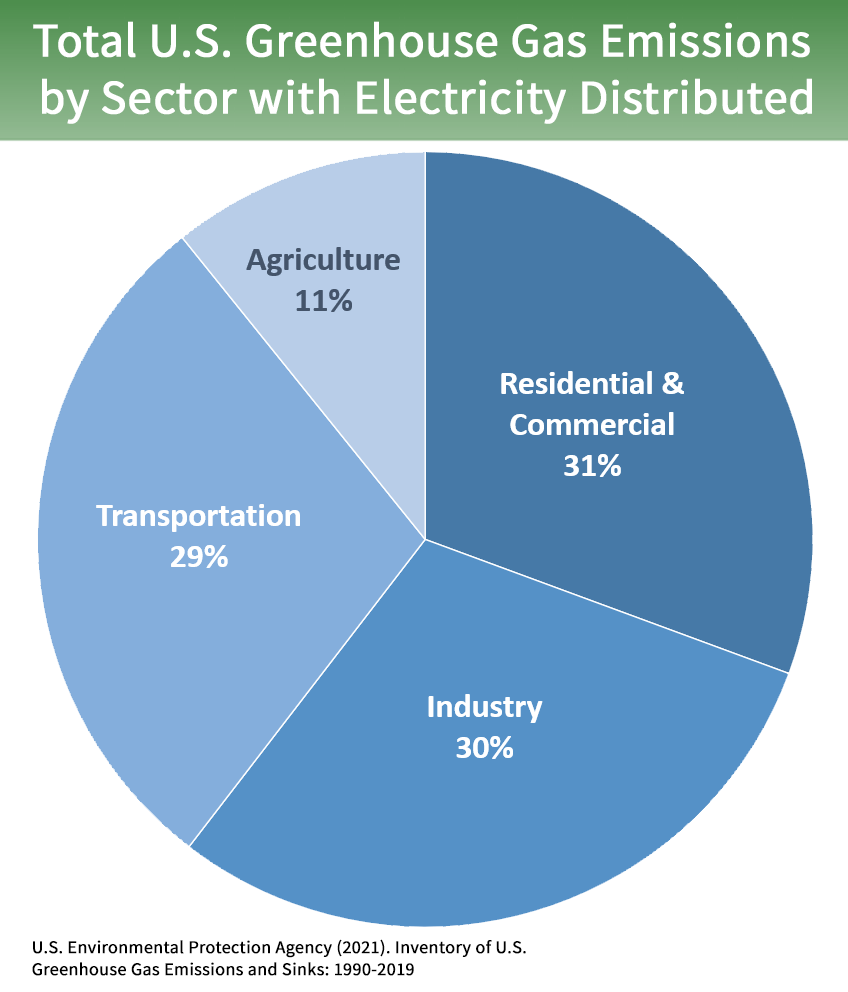



Sources Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Us Epa
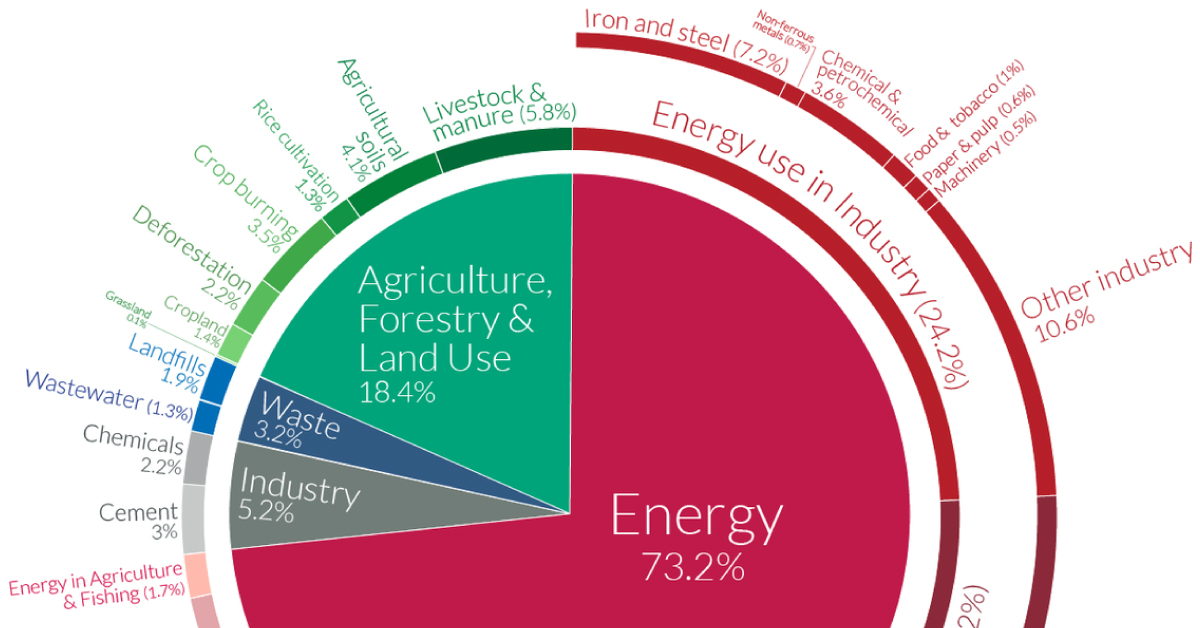



A Global Breakdown Of Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Sector




Mexico S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Have Increased By 74 Since 1990 Climate Scorecard




California S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Rose Slightly In 18 Los Angeles Times
コメント
コメントを投稿